Tags :
Schedule a Call Back

Vijay Shah, Managing Partner, India Precast, advocates the use of precast concrete as he puts forth details about its manufacturing, uses and methods while emphasising the sustainability of the product.
Explain the process of casting concrete in shapes and what is the grade of concrete used for making these shapes?
Precast casting concrete elements are manufactured with the required steel reinforcement either in formwork, moulds or on steel plates with side shuttering etc. The concrete cast is made at a different location and is then transported to the site. Precast elements are made of minimum M20 to M50 grade of concrete.
What is the difference between precast and cast in-situ as uses of concrete?
Tell us about prestressed and reinforced concrete.
Prestressed concrete is a combination of high strength concrete and tensioned steel strands. This combination makes a strong structural unit that is useful in building roof slabs, bridge girders etc. Reinforced concrete is manufactured from a combination of high strength concrete and normal reinforcement bars.
Tell us more about the precast elements manufactured, their shapes and sizes.
Precast is one of the best ways to rapidly build industrial buildings, commercial buildings, affordable housing, mass, EWS, LIG housing, schools, hospitals, public buildings, agriculture railways, stadiums, sport centres, parking, bridges, airports etc. They have a higher productivity and quality set at industry level.
Various types of precast elements manufactures are:
What is hollowcore concrete flooring and what is its lifespan?
Hollowcore slabs are precast, prestressed concrete elements that are generally used for flooring. Some of the advantages of using these flooring are longer lifespans and no propping, flexibility in designs, faster construction, lightweight structures, fire resistant structures, high load capacities and units manufactured specific to the project.
The maximum span of hollowcore floors will depend on the floor depth and the specific loadings imposed on the floor.
What are the quality standards followed while making precast shapes for any project?
Quality control is a very important aspect in the process of making precast concrete shapes. It is imperative to make precast shapes as per the exact requirement provided by the engineers and the construction party. To maintain the quality of product from our end,
As precast use of concrete is conducted in a dedicated space and is in a monitored environment, it becomes easier to maintain high quality due to its repeatability factor. The necessary general precast machinery and moulds, steel tables, concrete batching and dispensing equipment, vibrating and finishing equipment and dedicated labour team help maintain the higher quality standards as compared to cast in-situ use of concrete.
How do you incorporate sustainability in the process of precasting?
Precast use of concrete promotes sustainability with its repeatability factor. There’s more planning involved in the process and equipment like the moulds, vibrating machine, finishing machine are all reusable elements of the process.
As mentioned, there is planning in precast use of concrete where only the required measure of concrete is mixed and poured into moulds that are made to precision as per the requirement of the project. The quantity is also previously defined, which means there is reduced to zero wastage of material.
This waste reduction leads to lesser needs of cleaning and clearing equipment, which may further be fueled by other energy sources. Thus, precast concrete, by large, is a sustainable means of building.
What are the advantages of using precast concrete?
There are multiple advantages of using a precast structure for any project like cost efficiency, speed, versatility, safety, sustainability and beauty.
This includes:
What are the major challenges you face in the process of making precast shapes and in their transportation?
The precast industry plays on volume and repetition. This is one of the major challenges as well.
The requirement of having to repeat the process
that contains a large volume of mixed concrete and getting the same perfection in the shapes is a cumbersome process.
The initial investment in setting up the precast plant and acquiring all equipment and moulds is high. With bulk shapes to be transported from one place to another and the requirement for site space and handling, this time of concrete use is more suitable for tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
How do precast elements or shapes help in the profitability of a construction activity?
As precast concrete is made at a different location than the construction site, the other jobs keep going on at the site and then the precast shapes are placed there. This reduces construction time to up to one-third to one-fifth as compared to cast in-situ concrete, thus, reducing cost of the construction.
Construction maintenance is reduced as the quality of their precast structures are monitored and carefully administered at the plant level. This means it adds to the reliability, durability, accuracy, and ability to produce architectural elements in any building adding to its quality and strength. Precast also provides insulation, thermal inertia and fire resistance and the possibility of integration with MEP (Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing) from the start of the project.
How can precast concrete contribute towards affordable mass housing in India?
Defined shapes and technical requirements in precast concrete helps reduce the waste and increase the repeatability factor, thus, reduces the cost and time for any construction or building project. Higher control on quality, less time consumer leads to lesser need of labour and equipment on-site, which also adds to the profitability of the structure.
All factors combined bring down the overall cost of the project, leading to that benefit translating to the end consumer and bringing a surge of affordable mass housing in India.
-Kanika Mathur
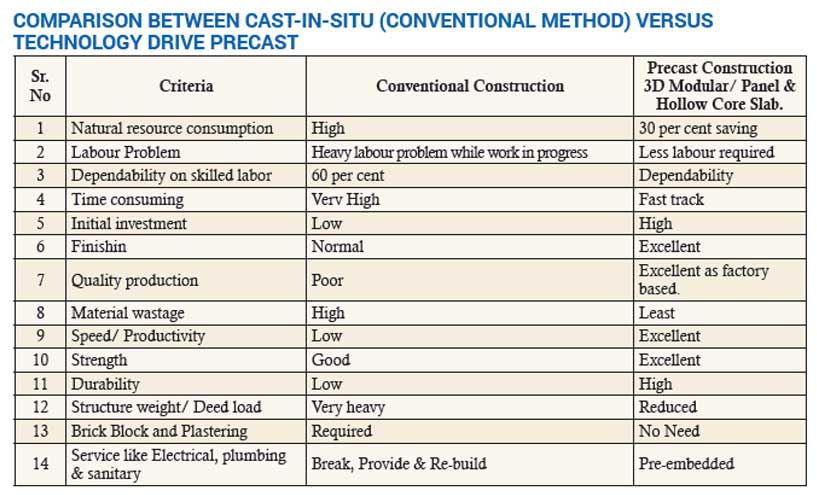
Comparison Between Cast-in-situ (conventional method) versus Technology Drive Precast
Sr. No Criteria Conventional Construction Precast Construction 3D Modular/ Panel & Hollow Core Slab.
1 Natural resource consumption High 30 per cent saving
2 Labour Problem Heavy labour problem while work in progress Less labour required
3 Dependability on skilled labor 60 per cent Dependability
4 Time consuming Verv High Fast track
5 Initial investment Low High
6 Finishin Normal Excellent
7 Quality production Poor Excellent as factory based.
8 Material wastage High Least
9 Speed/ Productivity Low Excellent
10 Strength Good Excellent
11 Durability Low High
12 Structure weight/ Deed load Very heavy Reduced
13 Brick Block and Plastering Required No Need
14 Service like Electrical, plumbing & sanitary Break, Provide & Re-build Pre-embedded


Subscribe to our Newsletter & Stay updated
Holcim has agreed to sell its Russian business to its local management. When the transaction is completed, the business will continue to operate u...
ACC Limited has won the National Award for Safety Excellence (FY2021-22) at the 10th Global Safety Summit (GSS) in the Large Enterprise-Cement Man...
ThyssenKrupp Polysius’ Asia Pacific division has secured an order for two Polflame-type main burners for an unnamed cement plant. The equipment ...